Get Complete Project Material File(s) Now! »
Thesis composition
Chapter 1 of this thesis provides a summary of plant defense responses and an up-to-date review of the NPR1 defense co-transcription factor. Various elicitors required for NPR1 activation, establishment of systemic acquired resistance and induction of pathogenesis-related gene products is reviewed. The rational, aim and objectives for carrying out this study is further outlined at the end of the introduction. In Chapter 2, the first objective to determine the expression pattern of two banana NPR1-like (MNPR1) genes and the subsequent response of downstream PR-1 and PR-3 gene expression in response to a hemi-biotroph is addressed.
Using quantitative realtime-polymerase chain reaction, the expression profiles of these genes are measured at specific time points in Xanthomonas campestris pv. musacearum-infected banana plants. In Chapter 3 comparative sequence analysis tools such as multiple sequence aligment and phylogenetics are used to campare the two banana NPR1-like coding sequences with 39 already identified and/or characterized plant NPR1-like sequences from genbank. Cis-regulatory elements within these two banana NPR1-like sequences are also identified and described in relation to their role in defense. Chapter 4 describes the procees of stably transforming Arabipdosis npr1-2 mutant plants with the two MNPR1 coding sequences under the control of the 35S cauliflower mosaic virus promoter and terminator sequences.
The basal transcript amounts of the MNPR1 coding sequences and of the Arabidopsis PR-1 gene are further determined in homozyous transgenic lines expressing the MNPR1 coding sequences. In Chapte 5, the response of the plants expressing the two banana NPR1 coding sequences to pathogen is evaluated in greater detail with specific emphasis on whether the difference in coding sequence within these two genes leads to differential response to various classes of pathogens (necrotroph,
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION
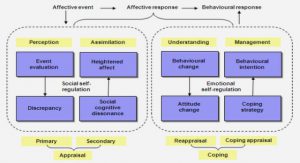
1.1 Plant defense responses
1.2 Types of defense responses
1.2.1 Basal resistance or innate immunity
1.2.2 Hypersensitive response
1.2.3 Systemic resistance
1.3 Deciphering metabolic components of the defense network
1.3.1 Role of the Non-expressor of pathogenesis-related1 genes
1.3.2 Structural analysis of the Nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related1 genes
1.3.3 Non-expressor of pathogenesis-related1 genes defense pathway
1.3.4 Non-expressor of pathogenesis-related1 genes interacting elements
1.3.4.1 Reactive oxygen species-antioxidant system and NPR1 interaction
1.3.4.2 Phytohormones and NPR1 interaction
1.3.4.3 Transcription factors and NPR1
1.3.4.4 Pathogenesis-related1 gene and NPR1
1.4 Working hypothesis and aim of study
CHAPTER TWO: SEQUENTIAL INDUCTION OF NPR-1 LIKE GENE EXPRESSION IN XANTHOMONAS INFESTED BANANA
2.1 Abstract
2.2 Introduction
2.3 Materials and methods
2.3.1 Plant growth, inoculation and sampling
2.3.2 Quantitative real-time-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.3.3 Data analysis
2.4 Results
2.4.1 MNPR1 induction in infected banana plants
2.4.2 PR-1 induction in infected banana plants
2.5 Discussion
CHAPTER THREE: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF TWO BANANA NPR1-LIKE CODING SEQUENCES
3.1 Abstract
3.2 Introduction
3.3 Materials and methods
3.3.1 Alignment of NPR1-like sequencea and identification of conserved region
3.3.2 Phylogenetic analysis
3.3.3 Identification of defense-response cis-elements with the MNPR1 coding region
3.4 Results
3.4.1 NPR1 sequence analysis and identification of conserved regions
3.4.2 Phylogenetic grouping of MNPR1 coding sequences
3.4.3 Comparison of defense-related cis-elements within the MNPR1 coding sequences
3.5 Discussion
CHAPTER FOUR: TRANSRMATION OF AN ARABIDOPSIS npr1-2 MUTANT WITH BANANA NPR1-LIKE CODING SEQUENCES
4.1 Abstract
4.2 Introduction
4.3 Materials and methods
4.3.1 Gene cassette design
4.3.1.1 Plasmids
4.3.1.2 MNPR1 cloning
4.3.2 Agrobacterium transformation
4.3.3 Transformation of npr1-2 Arabidopsis mutants
4.3.3.1 Growth of npr1-2 Arabidopsis mutant plants
4.3.3.2 Plant transformation
4.3.3.3 Screening of transformed lines
4.3.4 Transcription measurement
4.3.5 Statistical analysis
4.4 Results
4.4.1 MNPR1 gene cassette and Agrobacterium transformation
4.4.2 Transformation and selection of homozygous transgenic lines
4.4.3 MNPR1 and PR-1 gene transcription
4.5 Discussion
CHAPTER FIVE: CHARACTERIZATION OF TWO BANANA NPR1- LIKE CODING SEQUENCES FOLLOWING PATHOGEN INFECTION
CHAPTER SIX: NPR1-DEPENDENT PR-1 TRANSCRIPTION REQUIRES A FUNCTIONAL GLUTATHIONE BIOSYNTHETIC PATHWAY